A Review of PRP Effectiveness
Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) therapy has emerged as a promising treatment in regenerative medicine, leveraging the body's own healing mechanisms to address various musculoskeletal and dermatological conditions. By concentrating platelets from a patient's blood, PRP injections deliver growth factors that can accelerate tissue repair and reduce inflammation. However, the efficacy of PRP varies across different body parts and conditions.
PRP is prepared by drawing a small amount of the patient's blood, which is then processed to concentrate the platelets. These platelets release growth factors that stimulate tissue regeneration, and promote healing. The therapy is minimally invasive and is administered through injections directly into the affected area.
Clinical Uses and Evidence by Body Part
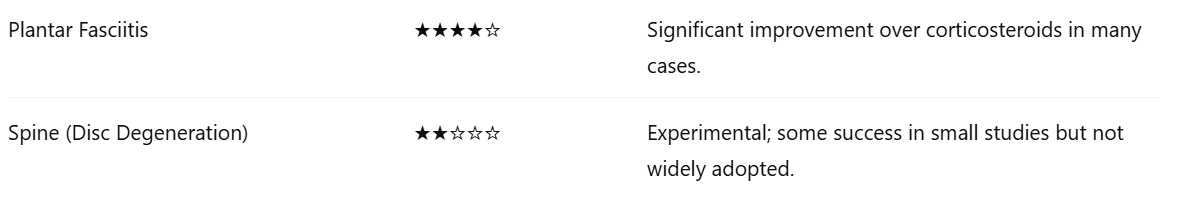
The following table summarizes the current evidence on the efficacy of PRP injections for various body parts:
Recent Studies and Meta-Analyses
Knee Osteoarthritis: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCTs) found that PRP injections provided significant pain relief and functional improvement compared to hyaluronic acid and saline, with effects lasting up to 12 months .(PubMed)
Rotator Cuff Tears: A systematic review and network meta-analysis indicated that PRP injections led to better long-term pain relief and functional improvement in patients with rotator cuff tears compared to corticosteroid and sodium hyaluronate injections .(BioMed Central)
Lateral Epicondylitis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of RCTs found that PRP injections significantly improved pain and function in patients with lateral epicondylitis, with effects lasting up to one year .(PubMed)
Achilles Tendinopathy: A meta-analysis of RCTs showed that PRP injections led to significant improvements in pain and function in patients with Achilles tendinopathy, with effects lasting up to 12 weeks .(MDPI)
Hair Restoration: A meta-analysis of clinical trials demonstrated that PRP therapy significantly increased hair density in patients with androgenic alopecia, with the number of treatments correlating with greater improvements .(PubMed)
Limitations and Considerations
While PRP therapy shows promise, several factors can influence its efficacy:
Preparation Technique: The method of preparing PRP can affect its concentration and potency.
Injection Protocol: The number of injections and their frequency can impact outcomes.
Patient Factors: Age, overall health, and the presence of comorbidities can influence healing responses.
Condition Severity: Chronic or severe conditions may require more intensive or repeated treatments.
Additionally, PRP therapy is not universally covered by insurance, and costs can vary widely.
PRP injections have demonstrated efficacy in treating various musculoskeletal and dermatological conditions, with the most robust evidence supporting their use in knee osteoarthritis, rotator cuff tears, lateral epicondylitis, and hair restoration. However, the success of PRP therapy depends on several factors, including the preparation technique, injection protocol, and patient-specific variables. Further research is needed to standardize treatment protocols and identify optimal patient populations.